In the manuals for modern electrical devices, especially powerful ones, you might find a section about the necessity of grounding. Today, we'll go into detail about the types of grounding, why it's needed, and what to do if it's absent.
Why is grounding necessary in a house?
While the equipment is in working order, its casing doesn't come into contact with current-carrying conductors or elements. But when a breakdown occurs, the insulation is compromised, and a dangerous potential can appear on the device's casing. A person touching such a device could receive an electric shock. Grounding is needed to remove this hazardous potential from the equipment.
Is grounding necessary?
The nature of electricity is such that current will flow through the path of least resistance to the earth, which maintains a zero potential. The electrical resistance of a human body is about 1000 ohms, whereas the resistance of a grounding conductor is 5-10 ohms. Therefore, with properly connected protective grounding, the current will flow not through the person's body but through the conductors into the ground. Hence, a protective system is extremely necessary.
Let's briefly consider how to establish grounding in a private house. It's better to conduct all the work during the initial planning and setup of the electrical system in the house; otherwise, you might need to replace the entire wiring with three- or five-core cables.
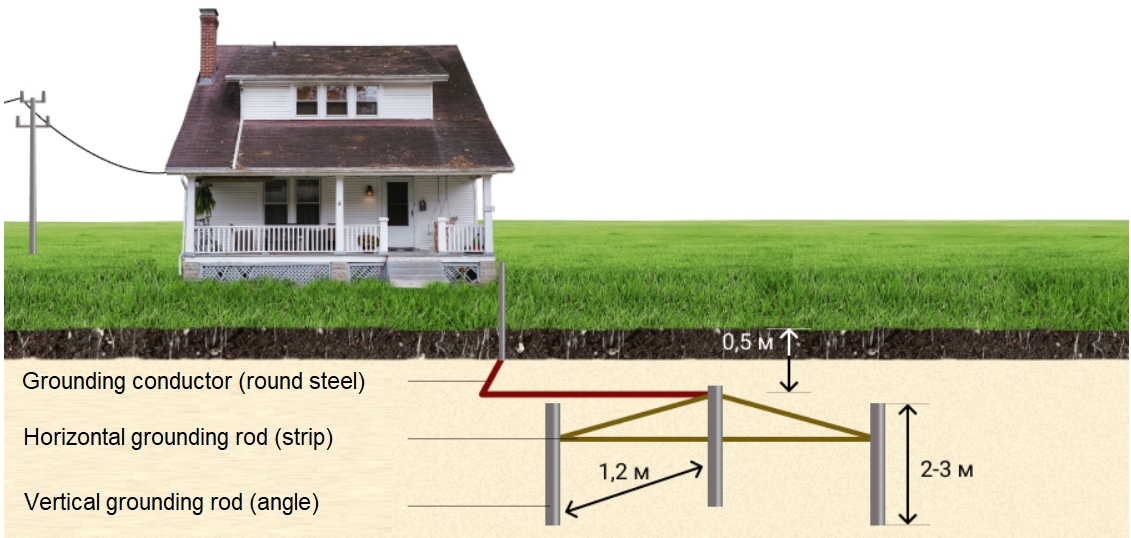
Grounding is done by burying several electrodes in the ground to a depth of about half a meter. Then they are interconnected with conductive elements (metal tape or rod), forming a sort of square or triangle. This construction is then connected to the house wiring by welding a cable to it.
How to ground an apartment?
To determine whether the apartment's wiring is connected to grounding and how to properly establish the connection, one needs to understand the types of grounding systems.
The rules for setting up and operating various grounding systems are outlined in the regulatory document, the Electrical Installation Code. To denote these systems, an abbreviation is used, employing the first letters of French and English words: ground - 'Terre,' neutral - 'Neuter,' isolated - 'Isole,' combined - 'Combined,' and separate - 'Separated.' The first letter in the system's abbreviation denotes the power station's grounding method, and the second one signifies the consumer.
Let's consider the existing systems:
- 1. Systems with an earthed neutral (TN). This system involves connecting protective and neutral conductors through a common earthed neutral at the substation. This means all consumers are connected to a common neutral conductor leading to the substation. These systems are divided into three types:
- TN-C. As evident from the abbreviation, this system uses a combined neutral conductor that combines the functional and protective neutral. Electric power from the substation is transmitted via four conductors - three phase and one neutral. Grounding occurs by connecting open conductive parts of devices to the neutral. However, this system always carries the risk of neutral failure, leading to voltage appearing on the device casings, which is its primary weakness.
- TN-S. Electricity from the substation is supplied via a cable with five conductors: three phase, neutral, and protective. Separate usage of the working and protective neutral is more effective for protection against electric shock. However, the need for a five-conductor cable significantly increases the cost of such a system.
- TN-C-S. This system was developed to reduce costs while retaining the advantages of the TN-S system. It's used in modern homes. Electricity is transmitted from the power station using a combined PEN conductor. At the house's entrance, the PEN conductor is split into protective (PE) and neutral (N). Apartments are connected using a three-core cable. The PE wire is connected in all electrical outlets and bolted to the grounding busbar. Connecting multiple conductors to the grounding busbar in a single connection point is prohibited.
- System with double grounding (TT). This system assumes the presence of a grounding circuit not only at the substation but also on the consumer side. It's used in cases where other methods are not feasible, such as in rural areas where electricity is transmitted via overhead lines.
- Systems with isolated neutral (IT). The peculiarity of this system is the absence of a neutral conductor and the mandatory presence of a grounding device on the consumer side.
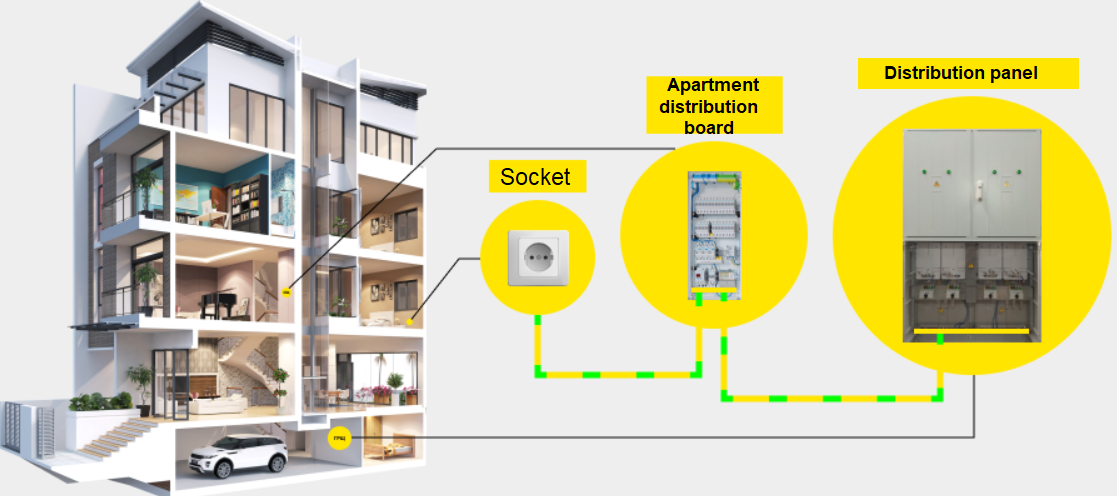
Before connecting electricity to your apartment, find out which system your house is connected to, and based on that, connect the apartment's distribution board. Proper connection will help achieve a high level of protection against potential electric shock.
What to do if there's no grounding?
In houses built during the Soviet era, where electricity is connected via a TN-C system using combined protective and neutral conductors, grounding in the apartment's distribution boards is absent, and electricity is supplied to the apartment via two-wire cables.
In such a situation, protection against electric shock for individuals can only be ensured by installing a residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) or residual current device (RCD) on all lines.
What grounding could be dangerous?
- Under no circumstances should grounding be done by attaching a cable to the plumbing or heating system. This could be dangerous not only for the apartment's residents but also for neighbors. In case of a current leak to the electrical appliance casing, it could transfer through the plumbing/heating system, posing a risk of electric shock to anyone using the water supply.
- Additionally, connecting the grounding contact to the neutral in the socket is strictly prohibited. If the neutral wire fails, hazardous voltage could appear on the casings of all electrical appliances.
- It is categorically forbidden to connect more than one conductor to a single PE terminal. In the event of a current leak in such a connection, there's a high probability that the electricity won't go to the ground via the protective conductor but may flow to other connected equipment.
Why is grounding indispensable?
In a modern home, there's a variety of small and large household appliances. All of them are connected to electricity, which means they can be hazardous in case of a malfunction. Installing voltage relays helps protect the appliances from voltage surges, ensuring their stable operation for a long time. However, despite the installation of relays, appliances sometimes malfunction and can be dangerous. Properly connected grounding helps protect individuals from electric shock.
Life and health are invaluable. Don't take risks—trust the connection of electricity only to professional electricians and quality electrical equipment!
(с) ds-electronics.com
